Introduction
This guide covers Google Tag Manager's role in website tag management and event tracking. From fundamentals to advanced applications, learn GTM core configuration skills. Through systematic learning, you'll improve tag management efficiency, analytics integration quality, and team collaboration, achieving better data collection and marketing results.
What Is Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is Google's free tag management system, allowing website administrators to manage tracking codes and marketing tags through a visual interface without modifying source code. GTM's core value lies in separating tag management from development, enabling marketers and analysts to deploy, test, and update tags independently, significantly improving efficiency and flexibility. Through GTM, you can centrally manage codes for Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, Mixpanel, PostHog, and other third-party tools, achieving unified tag management.
GTM solves core pain points in traditional tag management: each code addition or modification requires developer involvement, creating cumbersome and error-prone processes. With GTM, non-technical staff can deploy tags through simple configuration, while GTM provides version control, preview debugging, and rollback features, ensuring tag configuration security and reliability. For websites integrating multiple analytics tools and marketing platforms, GTM is essential, improving efficiency and enabling unified tag management strategies.
How Google Tag Manager Works
GTM operates on the container concept, where each website corresponds to one GTM container with ID format GTM-XXXXXXX. After installing GTM code snippets, GTM asynchronously loads container configuration, deciding which tags should trigger based on preset rules. GTM's core mechanism includes: tag configuration defines actions (e.g., sending data to Google Analytics), triggers define execution conditions (e.g., page load, button click), variables provide dynamic data (e.g., page URL, user ID), and the data layer serves as a bridge between website and GTM, allowing websites to actively push events and data.
GTM loads asynchronously without blocking page rendering, ensuring website performance. When pages load, GTM initializes the data layer, loads container configuration, and evaluates which tags should execute based on current page trigger conditions. This rule-based execution mechanism makes GTM flexible, enabling different tag combinations for different pages and user behaviors. GTM also supports server-side deployment (Server-Side GTM), moving tag execution from client to server, further improving performance and privacy protection.
GTM Core Components
GTM consists of five core components, each with specific functions. Understanding these components' relationships and usage is key to mastering GTM. Containers are GTM's foundation, tags define actions, triggers control timing, variables provide dynamic data, and the data layer connects websites and GTM. These components work together, forming GTM's powerful tag management capabilities.
Container
Containers are GTM's foundation, with each website corresponding to one container (ID format GTM-XXXXXXX). Containers include all tag, trigger, and variable configurations, serving as GTM's core management objects. After creating a container, you receive two code snippets: one for the <head> tag, another for the <body> tag start. Containers support version control, creating new versions with each publish, allowing rollback to previous stable versions. One GTM account can manage multiple containers, suitable for managing multiple websites or different environment configurations.
Tags
Tags define specific actions GTM executes, such as sending data to Google Analytics, triggering Facebook Pixel events, loading third-party scripts. GTM provides rich built-in tag types, including Google Analytics 4, Google Ads, Custom HTML, Custom Image. Each tag requires trigger configuration, executing only when trigger conditions are met. Tags can configure multiple triggers using "OR" logic, triggering when any condition is met. Tags also support priority and execution order control, ensuring critical tags execute first.
Triggers
Triggers define tag execution conditions. GTM provides multiple trigger types: Page View triggers on page load, Click triggers on element clicks, Form Submission triggers on form submissions, Custom Event triggers listen to data layer custom events. Triggers support complex condition combinations, setting multiple conditions using "AND" or "OR" logic. Triggers can also set exception conditions, excluding specific trigger scenarios. Proper trigger configuration ensures accurate tag execution.
Variables
Variables provide dynamic data usable in tags and triggers. GTM offers rich built-in variables, such as page URL, page title, click elements, form fields. You can also create custom variables, retrieving data from data layer, cookies, JavaScript variables. Variables support multiple data types: text, numbers, booleans, lists. Variables can use regular expressions, string operations for data processing. Proper variable use makes tag configuration more flexible and reusable, reducing duplicate configuration.
Data Layer
The data layer is a bridge between websites and GTM, a JavaScript array object storing and passing data. Websites can push events and data to the data layer using dataLayer.push(), and GTM can listen to these events and trigger corresponding tags. Typical data layer applications include: pushing page view events, pushing user interaction events (e.g., button clicks, form submissions), pushing business data (e.g., order amounts, product information). The data layer enables websites to actively pass information to GTM, achieving more precise event tracking. GTM also supports automatic data layer variable reading, simplifying data transfer.
GTM Use Cases
GTM has wide applications in website management and data analysis, from basic website analytics to advanced marketing automation. Below are GTM's main use cases, each with specific configuration methods and best practices.
Analytics Tool Integration
GTM's most common application is integrating analytics tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Through GTM GA4 tag configuration, you can track page views, custom events, conversion goals. GTM also supports integrating other analytics tools, such as Adobe Analytics, Mixpanel, PostHog, Amplitude. Using GTM to centrally manage these tools avoids duplicate tracking code in website code, improving code quality and maintenance efficiency. GTM also supports conditional triggering, deciding whether to load specific analytics tools based on page type, user attributes.
Marketing Tool Management
GTM is ideal for managing marketing tools, centrally managing tracking codes for Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, LinkedIn Insight Tag, Twitter Pixel. Through GTM configuration, you can uniformly manage conversion tracking, remarketing pixels, ad optimization events. GTM also supports dynamic parameter passing, dynamically setting ad parameters based on user behavior, page content, improving ad performance. Using GTM for marketing tools also simplifies compliance configuration, uniformly handling cookie consent and privacy settings.
Conversion Tracking
GTM's powerful event tracking makes it ideal for conversion tracking. You can configure form submission tracking, button click tracking, page view tracking, scroll depth tracking. GTM supports complex event condition evaluation, precisely identifying conversion behaviors, avoiding false triggers. Through data layer business data pushing, GTM can track order amounts, product information, user attributes, providing rich data support for marketing analysis.
User Behavior Analysis
GTM can track rich user behavior data, helping you understand how users interact with websites. Common user behavior tracking includes: scroll depth tracking (user scroll position), video playback tracking (play, pause, complete events), file download tracking (PDF, document downloads), external link click tracking, search behavior tracking. This behavior data helps optimize website content, improve user experience, identify user pain points, enhancing overall website performance.
Third-Party Tool Integration
GTM supports integrating numerous third-party analytics tools and marketing platforms, configuring these tools through a unified tag management interface without modifying source code. Below are common third-party tool configuration methods in GTM, each with specific configuration requirements and best practices.
Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is GTM's most commonly used analytics tool. When configuring GA4 tags, enter GA4's Measurement ID (format G-XXXXXXXXXX), found in GA4 management interface. GTM provides built-in GA4 Configuration tag type, with simple, intuitive configuration. After creating GA4 tags, select trigger conditions (usually All Pages), and GTM automatically tracks page view events. You can also configure GA4 Event tags to track custom events, such as button clicks, form submissions. GA4 integration with GTM is tight, supporting data layer pushing, user property settings, conversion event configuration. For detailed setup steps, refer to Google's official documentation.
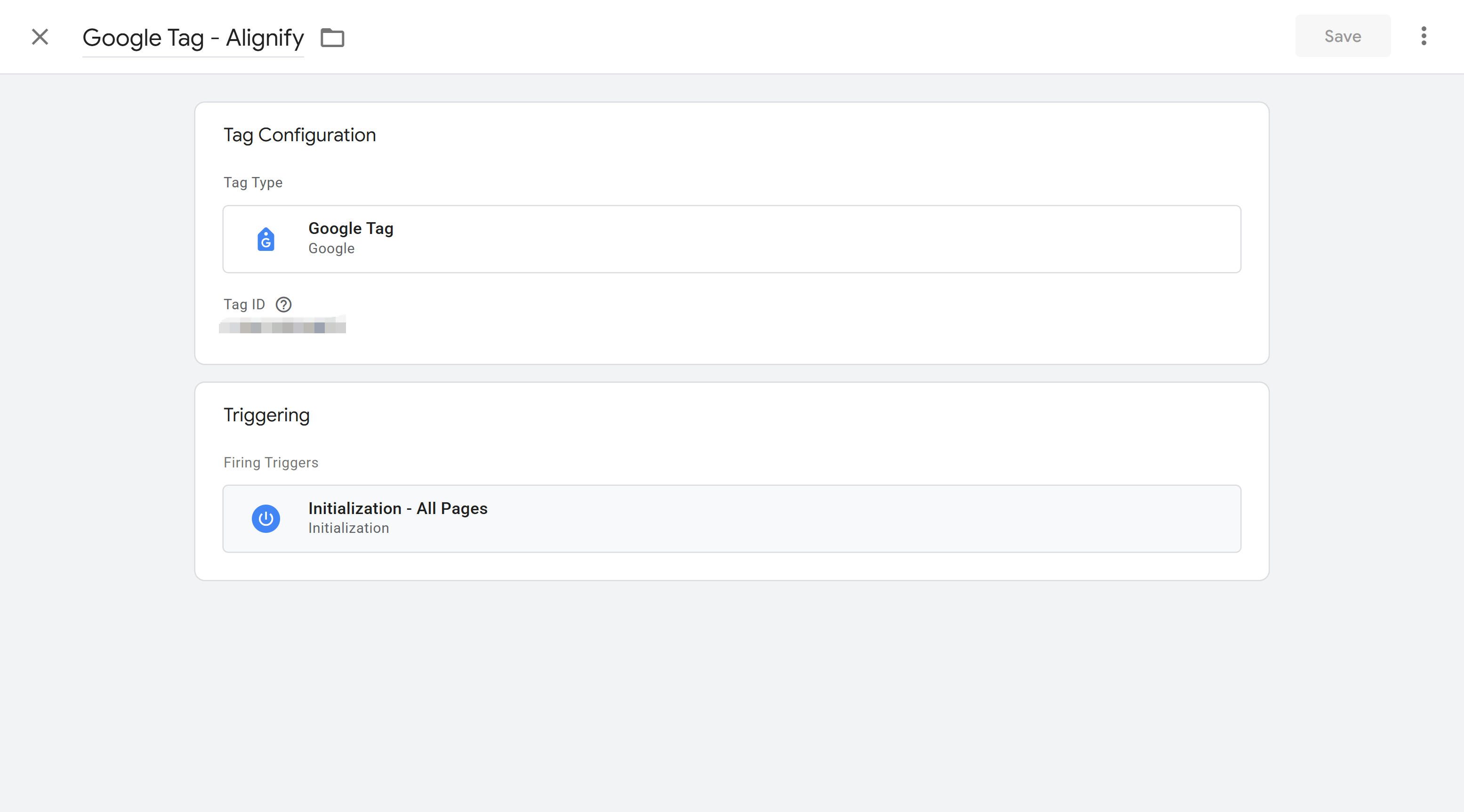
Google Ads
Google Ads tags track ad conversions and remarketing. When configuring Google Ads tags in GTM, enter Conversion ID and Conversion Label, found in Google Ads account conversion settings. GTM provides built-in Google Ads Conversion Tracking tag type, with relatively simple configuration. You can also configure Google Ads Remarketing tags for remarketing ad campaigns. Google Ads tags support dynamic conversion value passing, dynamically setting conversion values based on order amounts and business data, improving ad optimization. For complete setup guide, refer to Google's official documentation.
Facebook Pixel
Facebook Pixel tracks Facebook ad conversion effectiveness and user behavior. When configuring Facebook Pixel in GTM, use Custom HTML tag type, pasting Facebook-provided Pixel code. Facebook Pixel supports multiple event types, such as PageView, Purchase, Lead, triggered through data layer pushing or trigger configuration. GTM also supports Facebook Pixel's Advanced Matching feature, passing user email, phone numbers through data layer, improving match accuracy. When configuring Facebook Pixel, ensure privacy compliance, meeting GDPR and other regulations. For detailed integration steps, refer to Meta's official documentation.
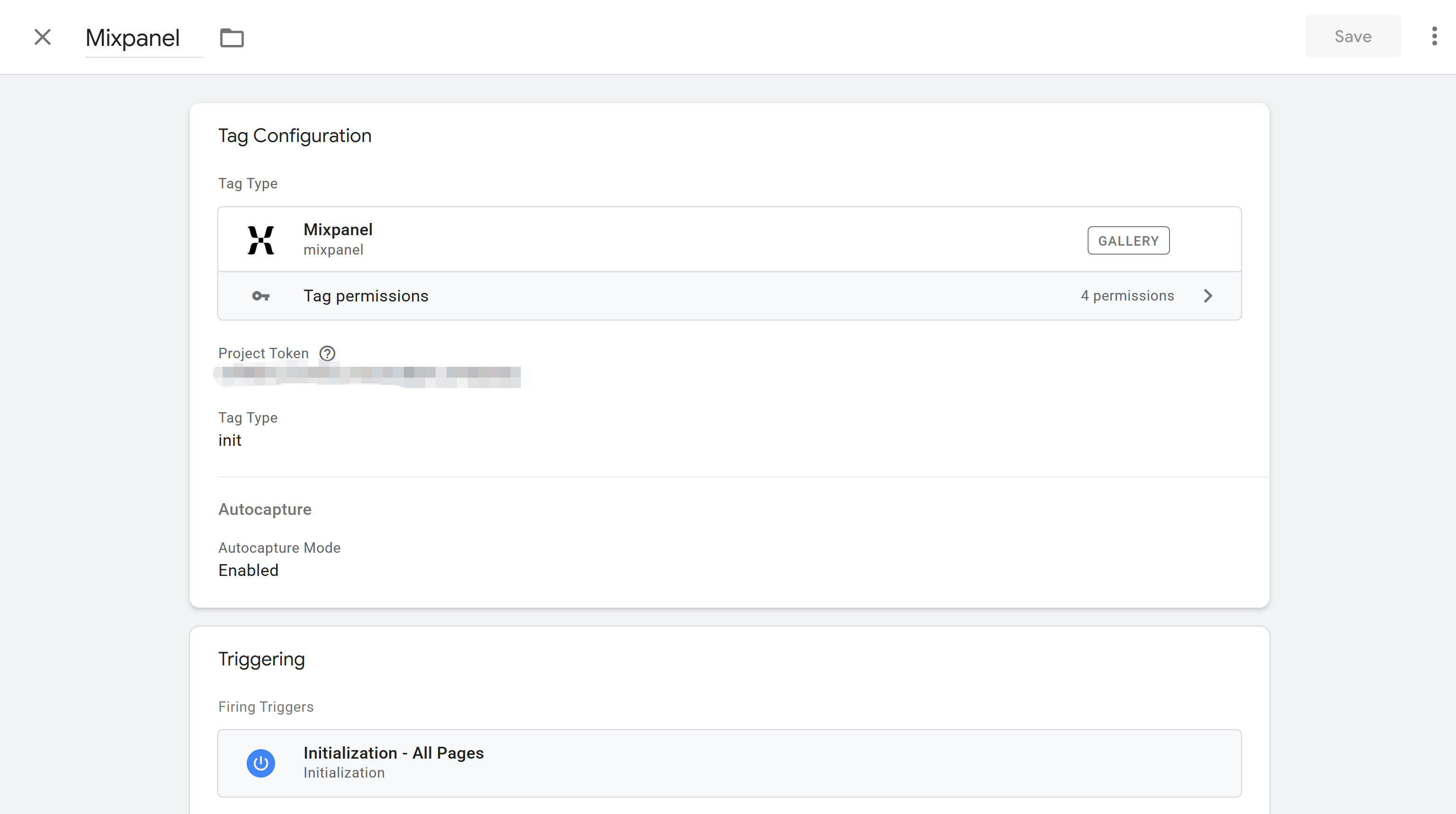
Mixpanel
Mixpanel is a powerful product analytics tool, integrable through GTM's Mixpanel template. First install Mixpanel template in GTM (search and add from community template library), then create Mixpanel initialization tag, enter Project Token, select Tag Type init. When creating page view tags, select Tag Type Track Pageview, trigger All Pages. Mixpanel also supports custom event tracking, configuring Track tag type, setting event names and properties. Mixpanel template supports user identification, user property settings, cohort analysis, ideal for product analytics scenarios. For complete GTM integration guide, refer to Mixpanel's official documentation.
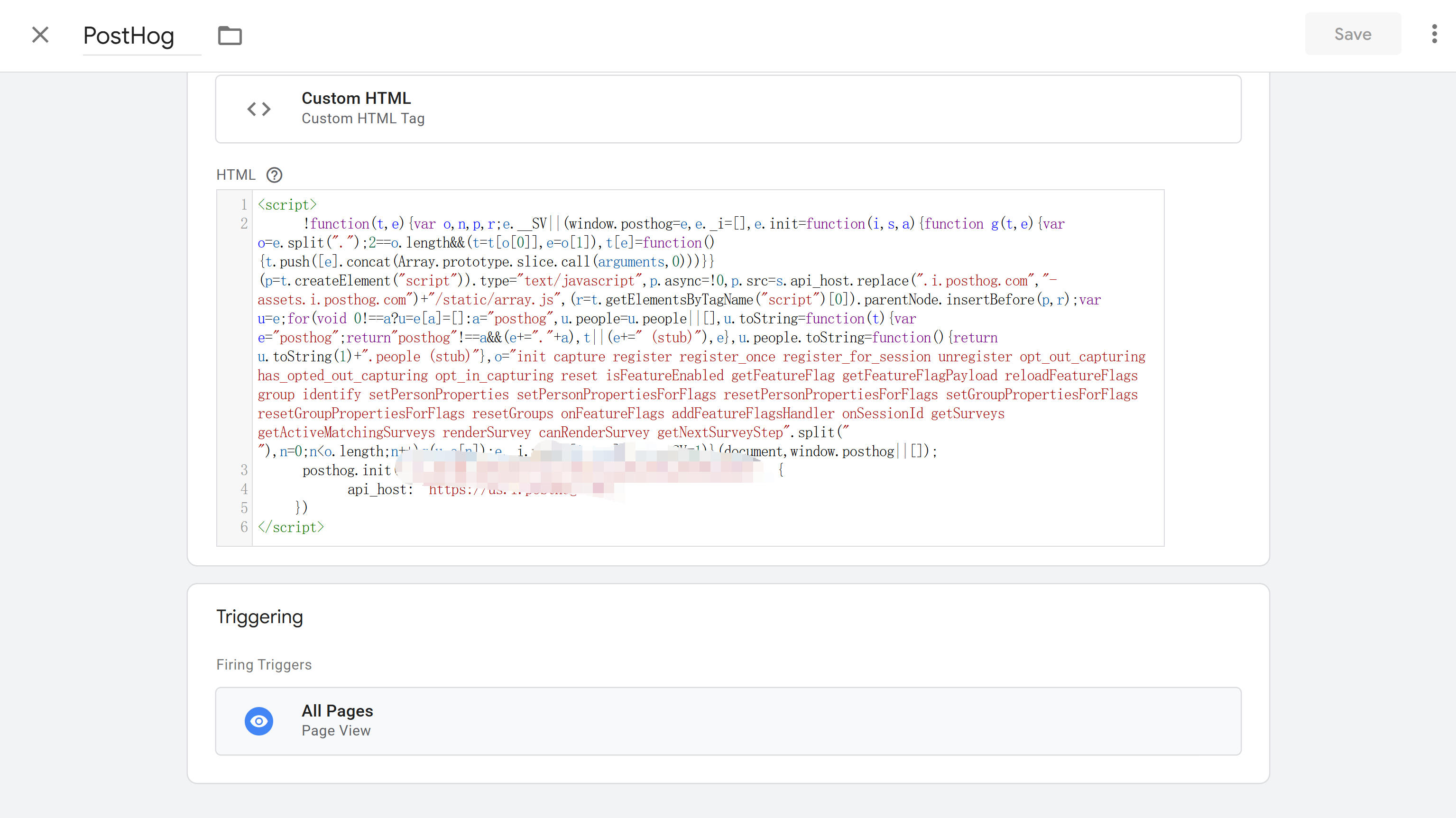
PostHog
PostHog is an open-source product analytics platform, integrable through GTM's Custom HTML tag. When configuring PostHog, obtain Project API Key and PostHog Host (usually us.i.posthog.com or eu.i.posthog.com), then create Custom HTML tag, paste PostHog initialization code. PostHog supports automatic capture, automatically tracking page views, clicks, form submissions. You can also push custom events through data layer, using posthog.capture() method to send event data. PostHog also supports Session Replay, Feature Flags, configurable through GTM. For detailed GTM integration steps, refer to PostHog's official documentation.
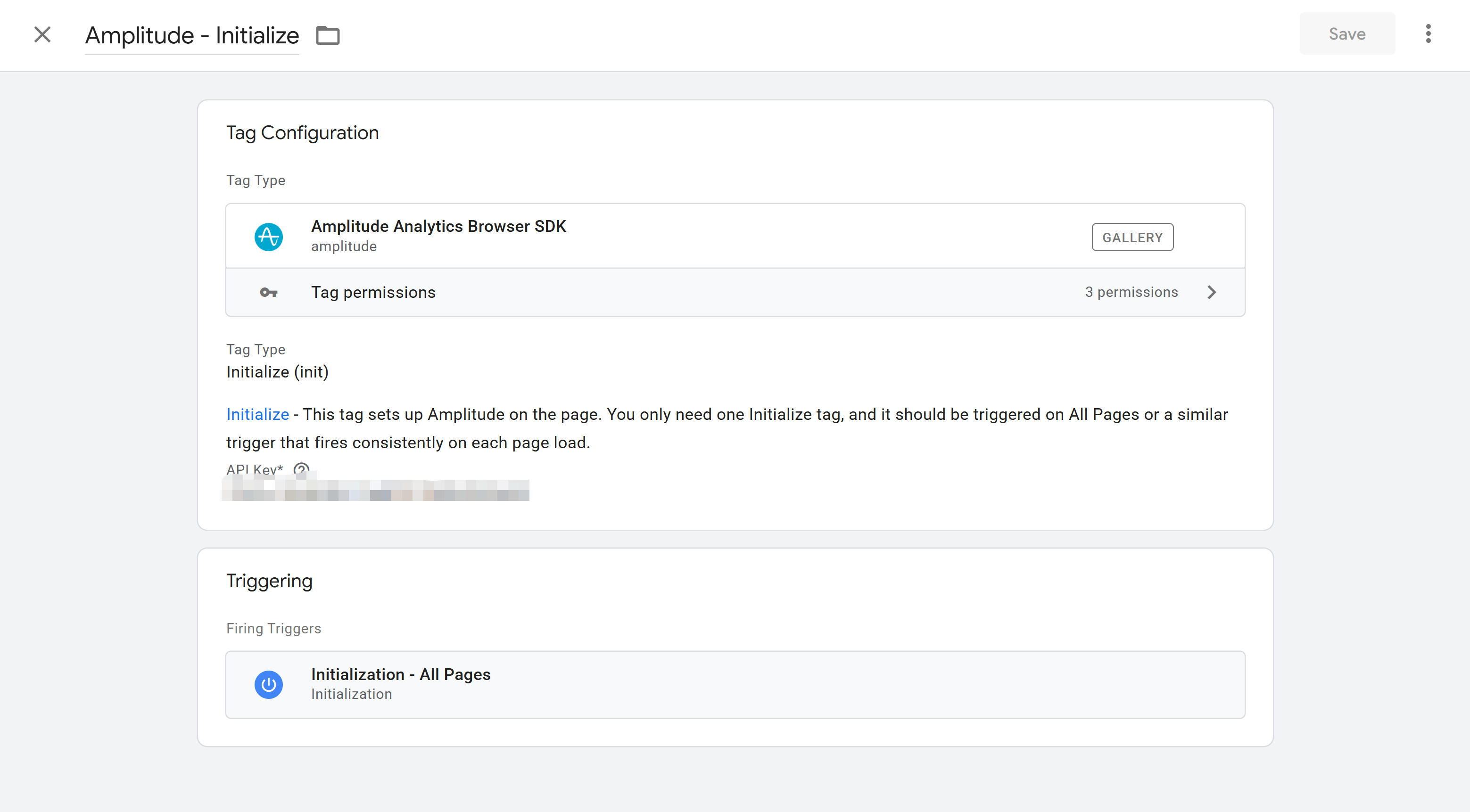
Amplitude
Amplitude is a professional product analytics platform, integrable through GTM's Amplitude template. First install Amplitude template in GTM (search and add from community template library), then create Amplitude tag, enter API Key. Amplitude template supports automatic capture, automatically tracking page views and user interactions. You can also configure custom event tracking, setting event names and properties. Amplitude supports user identification, user property settings, cohort analysis, powerful for product analytics and user behavior analysis. Amplitude template provides rich configuration options, customizable based on specific needs. For complete GTM template configuration guide, refer to Amplitude's official documentation.
GTM Setup and Deployment
GTM setup and deployment is relatively simple but requires following correct steps to ensure proper configuration. Below is GTM setup and deployment's complete process, from account creation to container publishing, with detailed instructions and considerations for each step.
Create GTM Account and Container
First visit Google Tag Manager website (tagmanager.google.com), log in with Google account. When creating new account, set account name and container name, select container type (Web, AMP, iOS, Android, Server). For websites, select Web container type. After creating container, you receive container ID (format GTM-XXXXXXX) and two installation code snippets. First snippet goes in website's <head> tag, second snippet goes at <body> tag start. These code snippets are GTM's foundation and must be correctly installed.
Install GTM Code to Website
When installing GTM code, ensure code exists on all pages, including homepage, inner pages, error pages. For websites using content management systems (CMS), add GTM code in template files. For frameworks like Next.js, add in root layout file. After installing code, use GTM's Preview mode to verify installation. Preview mode displays current page's container configuration, triggered tags, used variables, important for debugging GTM configuration.
Configure First Tag
Configuring first tag is important for learning GTM, recommended starting with Google Analytics 4. When creating GA4 tag, enter GA4's Measurement ID (format G-XXXXXXXXXX), select configuration tag type (Config or Event), set trigger conditions (usually All Pages). After configuration, use Preview mode to test tag triggering, then verify data reception in GA4's real-time reports. This process helps familiarize with GTM's basic operations, laying foundation for subsequent complex configurations.
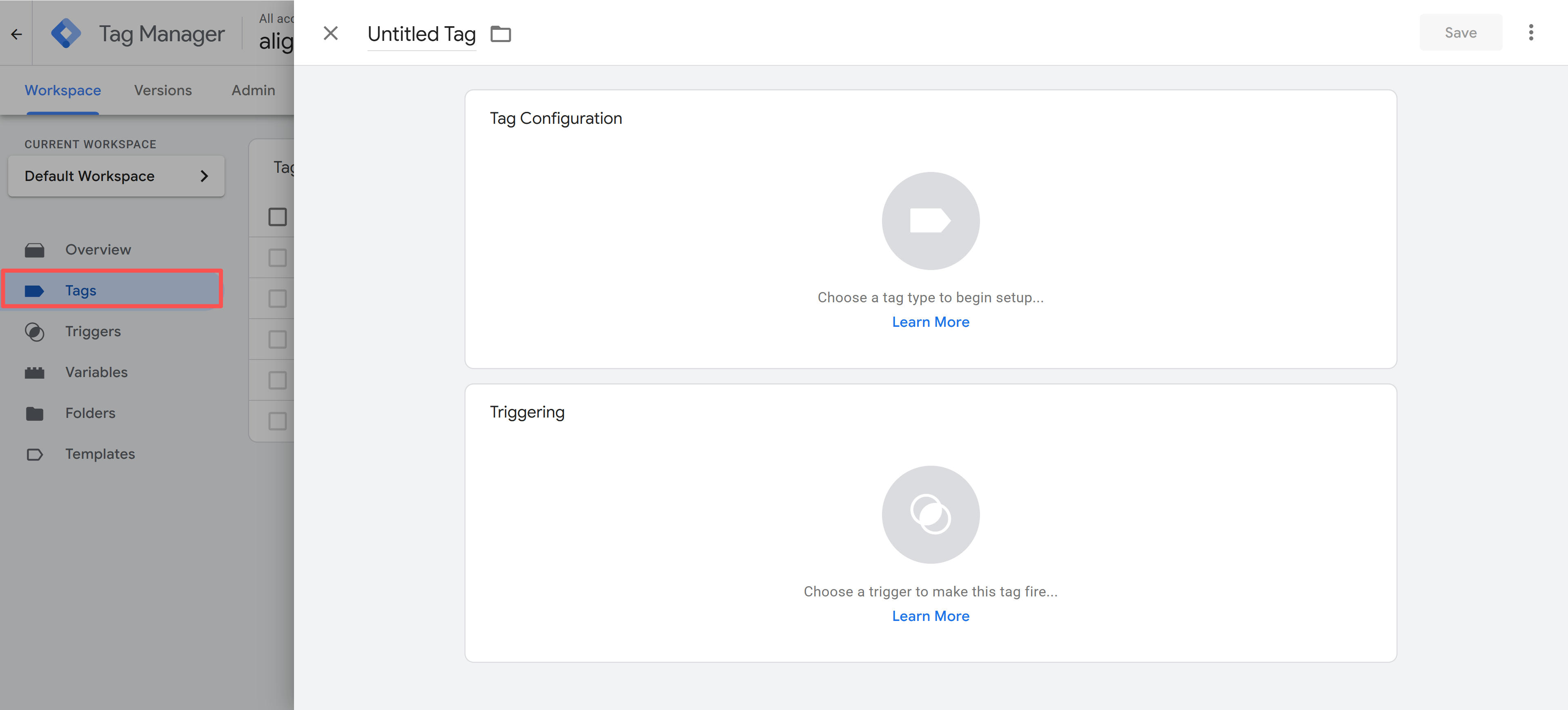
Test and Verify Configuration
GTM provides powerful testing and verification tools. Preview mode allows testing configuration before publishing, viewing tag triggering, variable values, data layer content. Debug mode provides more detailed debugging information, including tag execution order, trigger condition evaluation results, data transfer process. When verifying configuration, also check data reception in actual analytics tools, ensuring tag configuration correctness. GTM also supports version comparison, comparing configuration differences between versions, helping identify issues.
Besides GTM's built-in Preview and Debug modes, Google provides Google Tag Assistant browser extension, a powerful GTM verification tool. Tag Assistant can detect GTM containers, tag triggering, data layer content on pages, helping quickly identify configuration issues. After installing Tag Assistant, visit your website, extension automatically detects GTM configuration, displaying container ID, triggered tags, variable values, essential for GTM debugging.
Install Google Tag Assistant extension from Chrome Web Store. After installation, click Tag Assistant icon in browser toolbar, visit your website, extension automatically detects and displays GTM configuration. Tag Assistant also supports session recording, recording tag triggering during user operations, helping comprehensively understand GTM's working status.
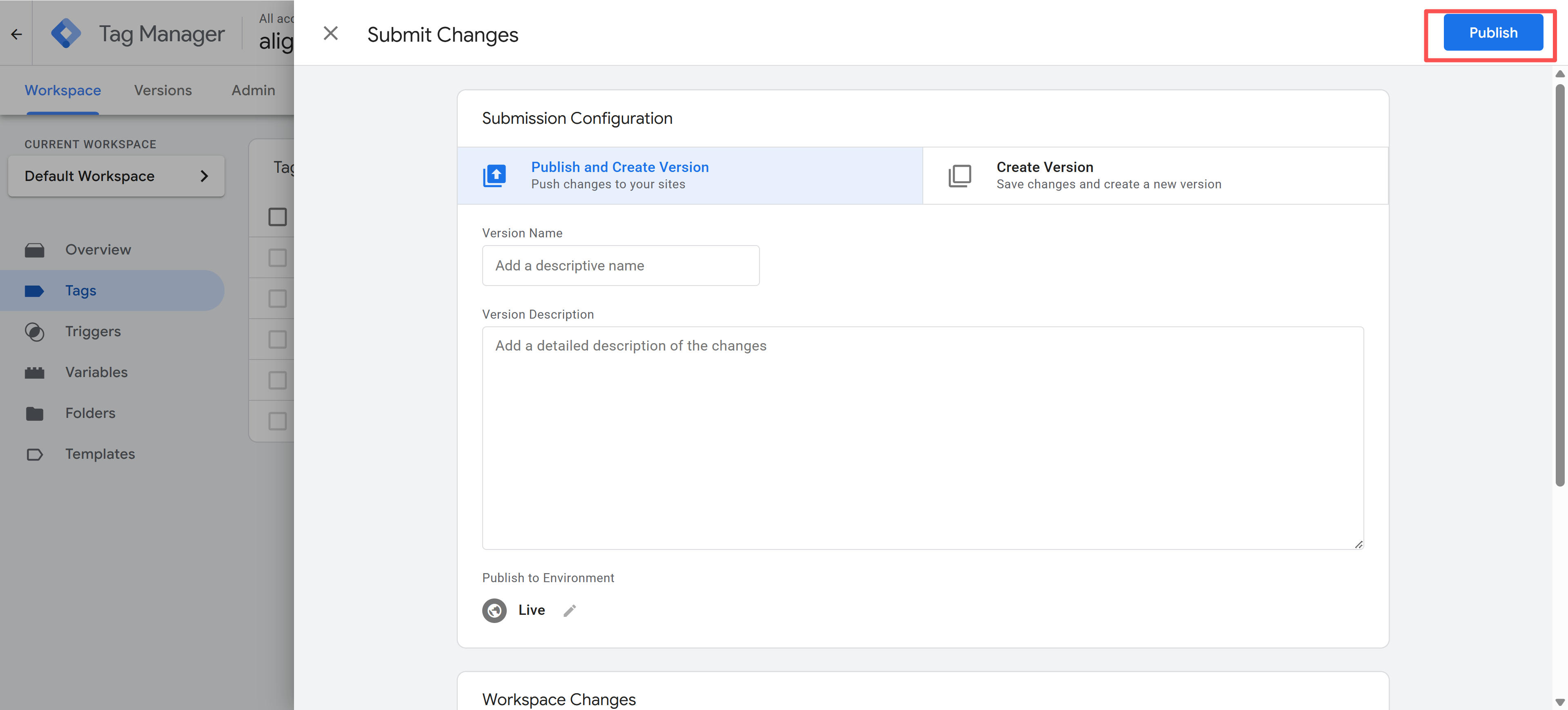
Publish Container
After testing, publish container. When publishing container, fill version name and description, explaining update content. After publishing, new configuration immediately takes effect, all website visitors use new configuration. GTM supports version rollback, quickly rolling back to previous stable version if new configuration has issues. Recommend thorough testing before each publish, recording change content in version description, facilitating subsequent maintenance and troubleshooting.
How to Choose and Use GTM
Choosing appropriate tag management solution and correctly using GTM is key to successful tag management. Below are key considerations and practical advice for GTM selection and use, helping make informed decisions and achieve efficient tag management.
1. Determine Whether to Use GTM
GTM suits scenarios needing multiple tracking tools, frequent tag configuration updates, non-technical staff involvement. If websites only need simple Google Analytics tracking with rare configuration changes, direct code deployment may be simpler. For websites integrating multiple analytics tools, marketing platforms, A/B testing tools, GTM is ideal. GTM also suits scenarios needing rapid tag deployment, frequent testing of different configurations, team collaboration.
2. Create and Configure GTM Container
Creating GTM account and container is first step, select Web container type, set clear container name. Install GTM code on all website pages, ensuring correct placement. Configure first tag (recommend starting with GA4), familiarize with GTM's basic operations. Use Preview mode to verify installation and configuration, ensuring tags trigger correctly. Establish tag naming and organization standards, laying foundation for subsequent tag management.
3. Configure Core Tags and Triggers
Configure core tags based on website needs, such as page view tracking, conversion event tracking, user behavior tracking. Properly configure triggers, ensuring tags trigger at correct times. Use variables to simplify configuration, improving reusability. Establish data layer pushing mechanism, enabling websites to actively pass data to GTM. Configure tag priority and trigger order, ensuring critical tags execute first. Regularly test and verify tag configuration, ensuring accurate data collection.
4. Optimize Performance and Privacy Compliance
Optimize GTM configuration to improve performance, remove unnecessary tags, properly configure trigger conditions, use lazy loading strategies. Configure privacy compliance settings, use Google Consent Mode, integrate cookie consent management tools. Regularly review data collection scope, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations. Use server-side GTM (if applicable) to further improve performance and privacy protection. Establish performance monitoring mechanisms, promptly identifying and resolving performance issues.
5. Continuous Maintenance and Monitoring
Establish GTM maintenance processes, regularly check tag configuration, clean unused tags and variables. Use version control to manage configuration changes, recording each update's content and reasons. Monitor tag execution, promptly identifying and resolving issues. Regularly review data quality, ensuring tags work correctly. Establish team collaboration mechanisms, ensuring tag management standardization and consistency. Continuously learn and apply GTM best practices, constantly improving tag management levels.
Following this systematic usage process, you'll fully leverage GTM's advantages, achieving efficient tag management. Remember, GTM is not just a tool but a tag management methodology, requiring continuous learning and practice to master its essence.
Conclusion
Google Tag Manager, as modern website tag management's core tool, provides website administrators with powerful and flexible tag management capabilities. Through GTM, you can centrally manage various tracking codes and marketing tags, improving efficiency, reducing development team dependency, achieving faster, more flexible tag deployment and updates. GTM's core value lies not only in the tool itself but in workflow optimization and team collaboration improvements it brings.
From container management to tag configuration, from trigger settings to data layer applications, each GTM component has unique roles and value. Understanding these components' functions and relationships, mastering GTM usage methods, is key to successful GTM use. GTM's powerful features and flexibility make it ideal for modern website tag management, providing efficient, reliable tag management solutions for website administrators.
Recommend website administrators incorporate GTM into daily website management's important components, establish standardized tag management processes, continuously optimize configuration, ensuring data collection quality and reliability. Through systematic learning and practice, you'll fully leverage GTM's advantages, achieving more efficient, reliable website tag management.
References
Google Tag Manager. (2025). Google Tag Manager Help Center. Retrieved from https://support.google.com/tagmanager
Google Developers. (2025). Tag Manager Best Practices. Retrieved from https://web.dev/articles/tag-best-practices
Google Tag Manager. (2025). Server-Side Tagging. Retrieved from https://support.google.com/tagmanager/answer/13387731
Google Developers. (2025). Google Consent Mode. Retrieved from https://developers.google.com/tag-platform/security/guides/consent
