What are Meta Tags?
Meta Tags are elements in the HTML <head> section that provide metadata about web pages to search engines and browsers. These tags don't display directly in page content but are crucial for search engines to understand page content and decide how to index and display pages. They serve as a communication channel between website owners and search engines, conveying essential information about page purpose, content, and relevance to specific search queries.
Meta Tags play important roles in SEO. They help search engines understand page topics, content, and intent, affecting how pages appear in search engine results pages (SERP), influencing CTR and ranking performance. While not all Meta Tags are direct ranking factors, they indirectly affect SEO by influencing user experience and search result display. Well-optimized Meta Tags improve how pages appear in search results, making them more attractive to users and potentially increasing click-through rates.
This article focuses on two most important Meta Tags: Meta Title (Title Tag) and Meta Description. These tags directly affect search result display and are core SEO optimization elements. They are the first things users see in search results, making them critical for attracting clicks and driving traffic. Other important Meta Tags (like Meta Robots, Open Graph, Twitter Cards) are briefly introduced here, with detailed content in other dedicated articles.
Meta Title (Title Tag)
Meta Title, also called Title Tag, is the <title> element in HTML <head>, defining the page title. This title displays in browser tabs, bookmarks, and search engine results pages (SERP) as the clickable title. It serves as the primary identifier for your page in search engines, social media shares, and browser interfaces, making it one of the most visible and important SEO elements.
Note that Meta Title is not the H1 tag. H1 is the visible main heading in page content, displayed in page body; Meta Title is code in HTML <head>, not directly visible in page content. While both describe page titles, their purposes and display locations differ completely. H1 provides visual hierarchy within page content, while Meta Title serves as metadata for search engines and browsers, appearing in search results and browser tabs.
Also, Meta Title is not always the Title Link in search results. While Google usually prioritizes your Meta Title as the clickable title, if Meta Title doesn't match page content or fails to accurately describe the page, Google may use H1 or other page text as Title Link. According to the SERP guide, Google dynamically adjusts displayed titles based on content relevance and user search queries. Google may use AI to auto-summarize page titles, making accurate Meta Title descriptions more important. Your Meta Title should be optimized for keywords and accurately reflect page content to ensure Google uses it as intended.
In search results, Meta Title is usually the first line users see and a key factor in click decisions. An excellent Meta Title should accurately describe page content, include target keywords, be attractive, and encourage clicks. Meta Title is a key factor affecting CTR.
Meta Title affects SEO in two ways: first, it's an important signal for search engines to understand page topics—while Google says title tags aren't direct ranking factors, they help understand page content; second, an optimized Meta Title can improve search result CTR, and high CTR may signal positive user behavior, indirectly boosting rankings.
For Meta Title length, keep it between 50-60 characters. Exceeding this, Google may truncate titles in search results, hiding important information. Note this is a recommendation, not a hard limit—actual display length varies by device. Mobile displays are usually shorter, so place most important keywords and information within the first 50 characters.
When writing Meta Title, follow these principles: include target keywords but avoid keyword stuffing; accurately describe page content, avoid misleading users; match search intent (informational, navigational, or transactional); create unique titles for each page, avoid duplicates; include brand name (usually at the end) to enhance brand recognition.
Meta Description
Meta Description is the <meta name="description"> element in HTML <head>, providing a brief page description. This description usually displays in search engine results pages, below the title, giving users a page content preview.
While Google officially states Meta Description isn't a direct ranking factor, it remains very important for SEO. Meta Description's main value is affecting click-through rate (CTR)—an attractive and relevant description can significantly improve search result CTR, and high CTR may indirectly affect ranking performance.
CTR Importance: While Meta Title and Meta Description aren't direct ranking factors, they indirectly affect SEO through CTR. Data shows well-optimized Meta Tags can significantly improve search result CTR, and high CTR may signal positive signals to search engines, indirectly affecting rankings.
Meta Description length should be 120-160 characters. Exceeding this, Google may truncate descriptions in search results, hiding important information. Similar to Meta Title, mobile displays may be shorter, so place core information within the first 120 characters.
When writing Meta Description, follow these principles: accurately describe page content so users know what they'll see after clicking; include target keywords naturally; be attractive and encourage clicks; include call-to-action like "Learn more" or "Get started"; create unique descriptions for each page, avoid duplicates; highlight special value (free tools, detailed guides) if pages have them.
Note that even without writing Meta Description, search engines automatically extract text from page content as search result descriptions. While this won't cause penalties, auto-extracted descriptions may be less attractive and fail to convey page value effectively. Write unique Meta Descriptions for each important page to ensure search result descriptions attract clicks.
Other Important Meta Tags
Beyond Meta Title and Meta Description, other important Meta Tags are worth knowing. While these don't directly affect search result display like title and description tags, they're equally important for SEO and user experience in specific scenarios.
Meta Robots Tag controls how search engines crawl and index pages. Using <meta name="robots" content="noindex,nofollow"> can prevent search engines from indexing pages or following links. Common values include noindex (don't index page), nofollow (don't follow links), index (allow indexing, default), and follow (allow following links, default). This tag is important for controlling which pages should be indexed—thank you pages, privacy policy pages typically shouldn't appear in search results. For more on robots.txt and indexing control, see the robots.txt guide.
Meta Viewport Tag controls how pages display on mobile devices. Using <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> ensures pages scale and display correctly on mobile. While this tag doesn't directly affect SEO rankings, mobile-friendliness is an important Google ranking factor, making correct Viewport tag configuration crucial for SEO.
Open Graph Tags optimize social media sharing. When users share your pages on Facebook, LinkedIn, etc., Open Graph tags (like `og:title`, `og:description`, `og:image`) determine what appears in share cards. While these tags don't directly affect search rankings, they can improve social media share CTR, bringing more traffic.
Twitter Card Tags are similar to Open Graph but specifically for Twitter sharing. Configuring Twitter Card tags (like `twitter:card`, `twitter:title`, `twitter:description`) optimizes Twitter share card display.
Canonical Tag technically isn't a Meta Tag (it's a <link> element) but often discussed with Meta Tags. Canonical tag specifies the canonical URL, helping search engines understand which URL is the main version, avoiding duplicate content issues. This is important for handling URL parameters, HTTPS/HTTP versions, www/non-www versions. For more on URL optimization, see the URL optimization guide.
Hreflang Tag also isn't a Meta Tag but a <link> element for multilingual and regional targeting. Hreflang tells search engines page language versions and target regions, helping display correct page versions for different regions. This is important for multilingual sites and international SEO. For more on website structure optimization, see the website structure optimization guide.
Meta Title & Description Best Practices
Optimizing Meta Title and Meta Description requires balancing multiple factors: SEO needs, user experience, and search intent matching. Below are proven best practices.
Keyword Optimization Strategy: Naturally integrating target keywords in Meta Title and Meta Description is important, but avoid keyword stuffing. Keywords should appear in the title's first half—the part users and search engines focus on most. Use semantically related words and synonyms to help search engines better understand page topics. Meta Titles containing target keywords usually achieve better ranking performance.
Search Intent Matching: Different search query types have different intents—informational (users want to learn about a topic), navigational (users want to visit a specific site), or transactional (users want to purchase or perform actions). Meta Title and Meta Description should match target keyword search intent. For example, informational query pages should use words like "guide" or "how to," while transactional query pages should use "buy" or "price."
Uniqueness and Accuracy: Each page should have unique Meta Title and Meta Description, avoiding duplicates. Duplicate Meta Tags confuse search engines and reduce user experience, as users can't distinguish different pages from search results. Meta Tags must accurately describe page content, avoiding misleading users. If users click and find content doesn't match descriptions, they'll leave immediately, causing high bounce rates, bad for SEO.
Mobile Optimization: With mobile search prevalence, Meta Tag display on mobile devices is equally important. Mobile search results usually display fewer characters, so place most important information in Meta Title and Meta Description's first half. Ensure Meta Tags remain attractive and readable on mobile devices.
A/B Testing and Optimization: Meta Tag optimization is an ongoing process. Google Search Console shows CTR data for different pages, identifying underperforming Meta Tags. For important pages, conduct A/B tests, trying different Meta Descriptions, observing which descriptions achieve higher CTR. Regular review and optimization can significantly improve search result CTR.
| Element | Meta Title | Meta Description |
|---|---|---|
| Recommended Length | 50-60 characters | 120-160 characters |
| Main Function | Search result title, affects CTR | Search result description, affects CTR |
| Keyword Position | First half, near beginning | Naturally integrated, avoid stuffing |
| Brand Name | Usually at end | Optional, based on space |
| Call-to-Action | Usually not included | Recommended, improves CTR |
Real-World Examples
Below are Meta Title and Meta Description analyses of several actual pages on the Alignify website, helping you better understand how to optimize Meta Tags in practice.
Example 1: Breadcrumbs Page
Page: /en/seo/breadcrumbs
<title>Breadcrumbs SEO: Improve UX & Rankings | Alignify</title> <meta name="description" content="Learn breadcrumb types, SEO value, best practices, and technical implementation. Includes structured data markup, HTML implementation, and platform configuration guides.">
Analysis: This Meta Title length is moderate (about 32 characters), keywords "breadcrumbs" and "SEO" appear in the title's first half, brand name "Alignify" is at the end, following best practices. Meta Description length is about 100 characters, accurately describes page content, includes keywords "breadcrumbs," "SEO," "best practices," and explains page value (practical guides, technical implementation). Overall, this configuration well balances SEO needs and user experience.
Example 2: AI Image Tools Page
Page: /en/tools/image
<title>Best AI Image Tools 2025: Generation & Editing | Alignify</title> <meta name="description" content="2025 curated 20+ AI image tools: Midjourney, Flux, Stable Diffusion image generators, plus headshot generation, image enhancement, relighting editing tools. Each includes tutorials and use cases.">
Analysis: This Meta Title uses "2025 best" time identifier and attractive words, helping improve CTR. Keyword "AI image tools" appears in the title, but "Generation & Editing" phrasing could be more natural. Meta Description length is about 90 characters, lists specific tool names (Midjourney, Flux, Stable Diffusion), attractive to users searching these tool names. Description mentions "tutorials" and "use cases," clarifying page value.
Improvement Suggestions: Title's "Generation & Editing" could be more natural, like "Image Generation & Editing Tools." Description could add call-to-action like "View complete tool list now."
Example 3: Affiliate Marketing Guide Page
Page: /en/marketing/affiliate
<title>Affiliate Marketing Guide: AI/SaaS Promotion | Alignify</title> <meta name="description" content="AI/SaaS affiliate marketing guide: learn to build effective programs, master setup, tool selection, promotion channels, and pitfalls. Maximize affiliate potential, achieve zero-cost acquisition.">
Analysis: This Meta Title length is about 30 characters, keywords "affiliate marketing" and "AI/SaaS" are clear, target audience (AI/SaaS products) is clear. Meta Description length is about 95 characters, uses attractive words like "complete guide" and "learn to," lists page content (setup, tool selection, promotion channels, pitfalls), ends with "achieve zero-cost acquisition" as value proposition, very attractive.
Advantages: Description includes clear value proposition (zero-cost acquisition), very attractive to target users (AI/SaaS product operators). Description structure is clear, lists specific learning content, letting users know what they'll get after clicking.
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid
When optimizing Meta Title and Meta Description, some common mistakes affect SEO and user experience. Understanding and avoiding these helps create more effective Meta Tags.
Title Too Long or Short: Meta Title too long gets truncated by search engines, hiding important information; too short wastes available space, missing opportunities to convey more information. Keep between 50-60 characters, ensuring important keywords and information are within the first 50 characters. Similarly, Meta Description too long gets truncated, too short can't fully describe page value.
Missing or Duplicate Descriptions: Many sites don't write Meta Descriptions for all pages, or multiple pages use the same description. Missing Meta Descriptions let search engines auto-extract content, possibly less attractive; duplicate Meta Descriptions prevent search engines and users from distinguishing different pages, affecting user experience and SEO. Create unique Meta Descriptions for each important page.
Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords in Meta Tags makes content unnatural and unreadable. This affects user experience and may be seen as spam by search engines. Keywords should naturally integrate into Meta Tags, maintaining readability and attractiveness. Remember, Meta Tags' primary goal is attracting user clicks, not just satisfying search engine algorithms.
Clickbait: Using exaggerated or misleading titles and descriptions to attract clicks, but page content doesn't match descriptions. While this may improve CTR short-term, it causes high bounce rates and low user satisfaction, bad for SEO long-term. Meta Tags should accurately describe page content, avoiding misleading users.
Content Mismatch: Meta Tag descriptions don't match actual page content. This causes users to click and find content doesn't meet expectations, leaving immediately, causing high bounce rates. Search engines may see this as negative signals, affecting rankings. Ensure Meta Tags accurately reflect page content.
Ignoring Mobile Display: Only considering desktop display, ignoring mobile devices. Mobile search results usually display fewer characters—if important information is in Meta Tag's second half, it may not display on mobile. Place core information in Meta Tag's first half, ensuring key information is fully conveyed on all devices.
Using Site-Level Meta Tags
Problem: Many sites only set site-level Meta Title and Meta Description in root directory layout.tsx or global configuration, without configuring separately for each page. This causes all site pages to use the same Meta Tags, unable to accurately describe each page's unique content.
Impact: When all pages use the same Meta Tags, search engines can't distinguish different pages' content and topics, and users can't understand each page's specific content from search results. This affects SEO and reduces search result CTR, as users can't judge which result best meets their needs.
Solution: Create unique Meta Title and Meta Description for each page. In Next.js, configure metadata separately in each page's page.tsx, overriding site-level defaults. Ensure each page's Meta Tags accurately describe that page's content, topic, and value, helping users and search engines better understand pages.
Meta Title Misconfiguration Example
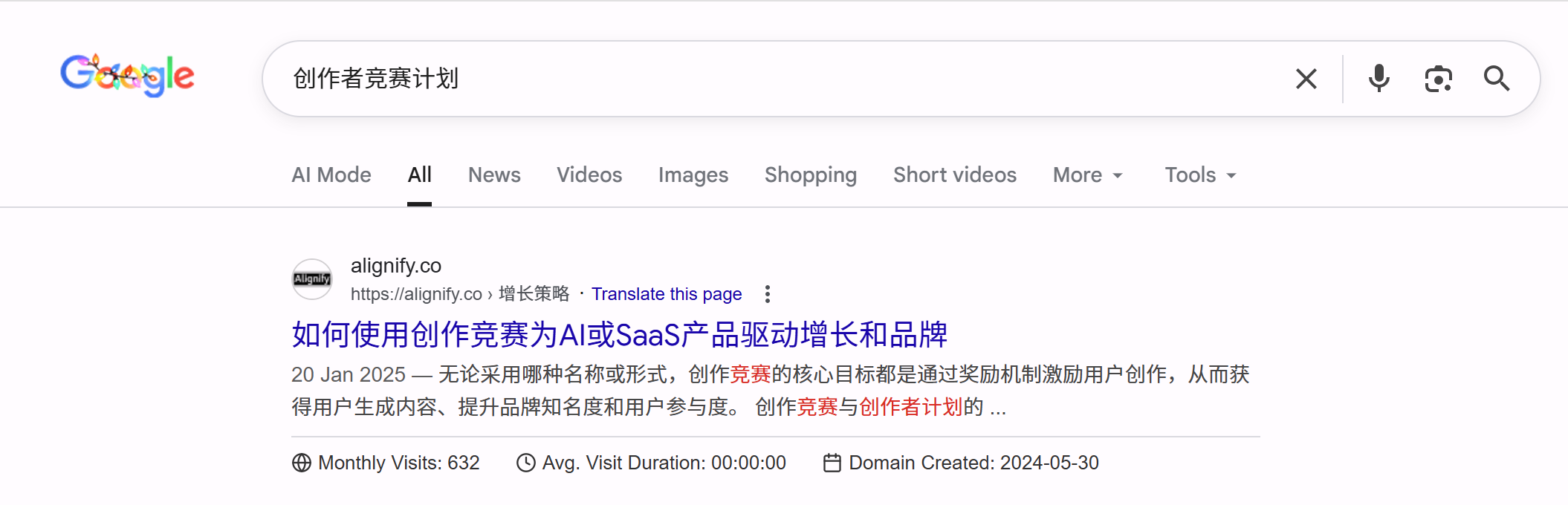
Below is a real-world example of Meta Title misconfiguration, showing problems misconfiguration can cause:
Minimax Website Configuration Issue: From the screenshot, Minimax website's M2 model page only uses "Minimax M2" as Meta Title, without any explanation. While M2 is Minimax's latest model, users can't understand from the title alone: 1. What is this: Users don't know what M2 is—product, service, or model; 2. Page content: Users can't understand what information this page provides—introduction, usage guide, or other content; 3. Value proposition: Title doesn't convey page's core value, can't attract clicks; 4. Missing keywords: Lacks "AI model," "large language model," "latest version" keywords, missing SEO opportunities.
Correct Approach: Use more descriptive Meta Title, e.g., "Minimax M2: Latest AI Large Language Model | Features & Usage Guide" or "Minimax M2 Model: 2025 Latest AI Model Introduction | Minimax." Such titles explain this is the latest model, include keywords, and let users understand page content, improving SEO and CTR.
Technical Implementation
Meta Tag technical implementation depends on your tech stack. Below are common implementation methods, including pure HTML and modern frameworks (like Next.js).
HTML Implementation
In traditional HTML pages, Meta Title and Meta Description are written directly in the <head> section:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Meta Tag SEO Guide: Title & Description | Alignify</title> <meta name="description" content="Learn Meta Title and Meta Description SEO optimization methods. Includes best practices, technical implementation, common mistakes, and complete guide to improve search result CTR and rankings."> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta charset="UTF-8"> </head> <body> <!-- Page content --> </body> </html>
The <title> tag defines the page title, displayed in browser tabs and search results. The <meta name="description"> tag defines the page description, usually displayed below the title in search results. Both tags should be in the <head> section, each page should have a unique Title and Description.
Next.js Implementation
In Next.js, use the Metadata API to configure Meta Tags. Next.js automatically converts these configurations to corresponding HTML tags. Below is this page's (`/en/seo/meta-tag`) actual configuration example:
// app/[locale]/seo/meta-tag/page.tsx
import { Metadata } from "next";
import MetaTagGuideEN from "@/blogs/MetaTagGuideEN";
export async function generateMetadata({ params }): Promise<Metadata> {
return {
title: "Meta Tag SEO Guide: Title & Description | Alignify",
description: "Learn Meta Title and Meta Description SEO optimization: best practices, technical implementation, common mistakes. Improve search result CTR and rankings.",
alternates: {
canonical: "https://alignify.co/en/seo/meta-tag",
languages: {
'zh': 'https://alignify.co/seo/meta-tag',
'en': 'https://alignify.co/en/seo/meta-tag',
},
},
};
}Next.js automatically converts `title` and `description` to corresponding HTML tags. `alternates` configuration sets Canonical URL and Hreflang tags, `openGraph` and `twitter` configurations optimize social media sharing. This approach is more concise and maintainable than manually writing HTML tags.
Dynamic Meta Tag Generation
For large websites, manually writing Meta Tags for each page is unrealistic. Use template systems or dynamic generation to auto-generate Meta Tags based on page content. For example, in Next.js use the `generateMetadata` function to dynamically generate Meta Tags:
// app/blog/[slug]/page.tsx
import { Metadata } from "next";
export async function generateMetadata({ params }): Promise<Metadata> {
const post = await getPost(params.slug);
return {
title: `${post.title} | Alignify`,
description: post.excerpt,
openGraph: {
title: post.title,
description: post.excerpt,
images: [post.image],
},
};
}This approach can auto-generate Meta Tags based on page data, ensuring each page has unique and accurate Meta Tags while reducing manual maintenance workload.
React + Vite Implementation
For projects using React + Vite (like Lovable), Meta Tag configuration requires special attention. While you can use react-helmet to dynamically set Meta Tags, this approach isn't SEO-friendly, as search engine crawlers may not correctly read client-side JavaScript dynamically generated Meta Tags when crawling pages.
react-helmet Issues: When react-helmet runs in client-side rendering (CSR) environments, Meta Tags are dynamically added to the DOM via JavaScript. When search engine crawlers crawl pages, if JavaScript hasn't finished executing, they may not see these Meta Tags, causing configured Meta Descriptions to be unrecognized and undisplayed by search engines.
Recommended Solutions: For React + Vite projects, here are better approaches:
1. Use Server-Side Rendering (SSR): If possible, consider using Next.js or other SSR-supporting frameworks. SSR can generate HTML containing Meta Tags on the server, ensuring search engine crawlers can directly read them.
2. Configure in index.html: For single-page applications (SPA), write basic Meta Tags directly in index.html. While this can't set different Meta Tags for each page, it at least ensures search engines can read basic SEO information.
3. Use Prerendering: Use tools like react-snap or prerender-spa-plugin to prerender pages at build time, generating static HTML files containing complete Meta Tags.
4. Use react-helmet-async: If client-side rendering is required, consider react-helmet-async, which provides better server-side rendering support. Note this still requires SSR to ensure SEO effectiveness.
Verify Meta Tags: After configuration, use Google Search Console's "URL Inspection" tool or browser developer tools to view page source code, confirming Meta Tags correctly appear in HTML's <head> section. If Meta Tags only appear after JavaScript execution, search engines may not correctly crawl them.
Multilingual Page Handling
For multilingual websites, create corresponding Meta Tags for each language version. In Next.js, configure different language version URLs through `alternates.languages`, and dynamically generate Meta Tags based on language through the `generateMetadata` function. Ensure each language version's Meta Title and Meta Description use the corresponding language and accurately describe that language version's content.
Tools & Checking Methods
Regularly checking and optimizing Meta Tags is an important part of SEO maintenance. Below are common tools and methods to help identify and fix Meta Tag issues.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides rich tools to check Meta Tag issues. In the "Enhancements" section, view structured data and other metadata status. In the "Coverage" report, see which pages lack Meta Descriptions. Through the "Performance" report, view CTR data for different pages, identifying underperforming Meta Tags.
Browser Developer Tools
The simplest direct checking method is using browser developer tools. In Chrome or Firefox, right-click the page, select "Inspect," then view the <head> section in the Elements tab to see all page Meta Tags. This is the most direct method to quickly check a single page's Meta Tag configuration.
Browser Tab Hover: The simplest method is hovering over the browser tab—the displayed tooltip text is that page's Meta Title. This is the most direct method to quickly check a single page's Meta Title.
SEO Tools
Professional SEO tools can batch-check Meta Tag issues across entire websites. Semrush Site Audit can check missing Meta Descriptions, duplicate Meta Titles, overly long Meta Tags, etc. Ahrefs Site Audit provides similar functionality. These tools quickly identify Meta Tag issues across entire websites and provide fix suggestions. For more SEO tool information, see the SEO tools guide.
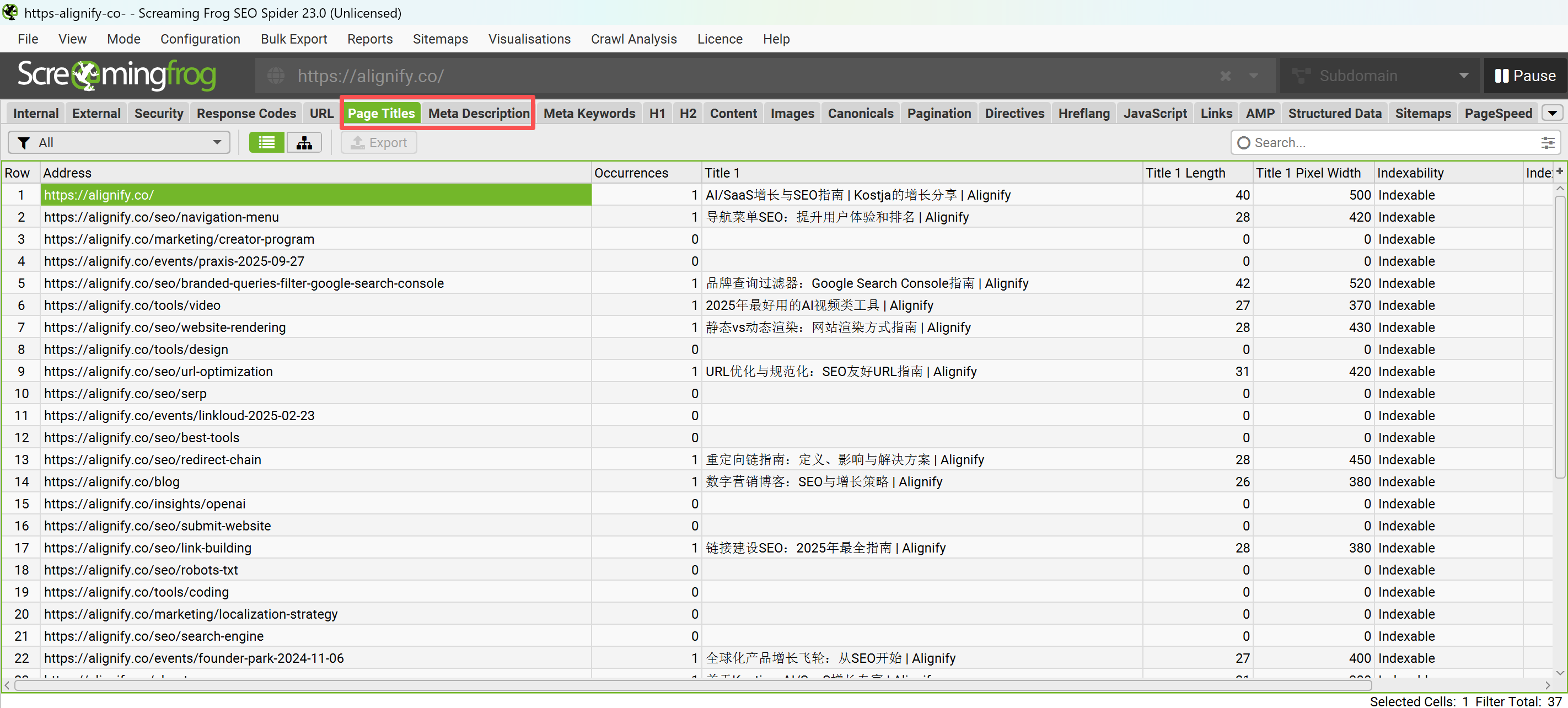
Screaming Frog SEO Spider: Screaming Frog is a powerful website crawler tool that can batch-check Meta Tag information across entire websites. By crawling websites, Screaming Frog can export all pages' Meta Titles, Meta Descriptions, H1 tags, etc., helping quickly identify missing, duplicate, or overly long Meta Tags. This is very useful for Meta Tag audits on large websites.
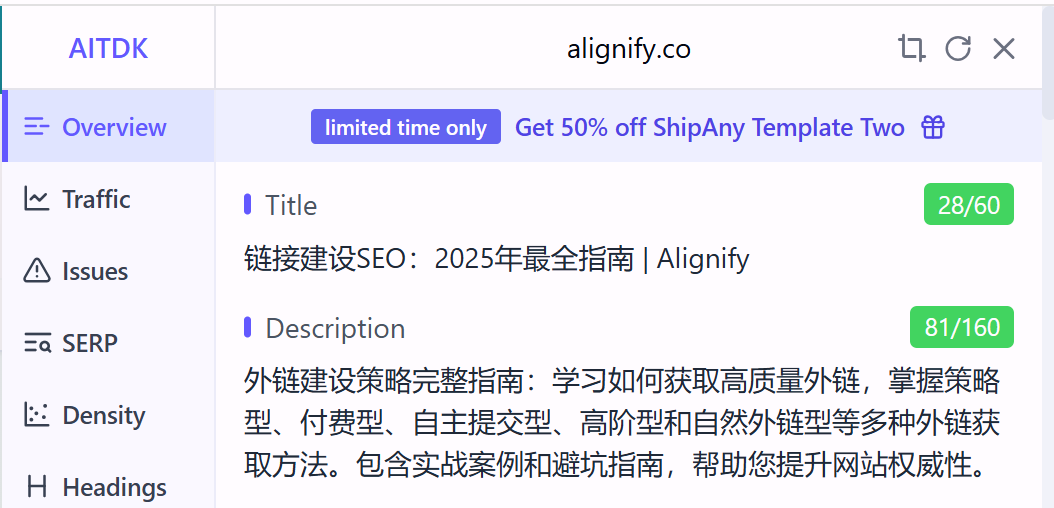
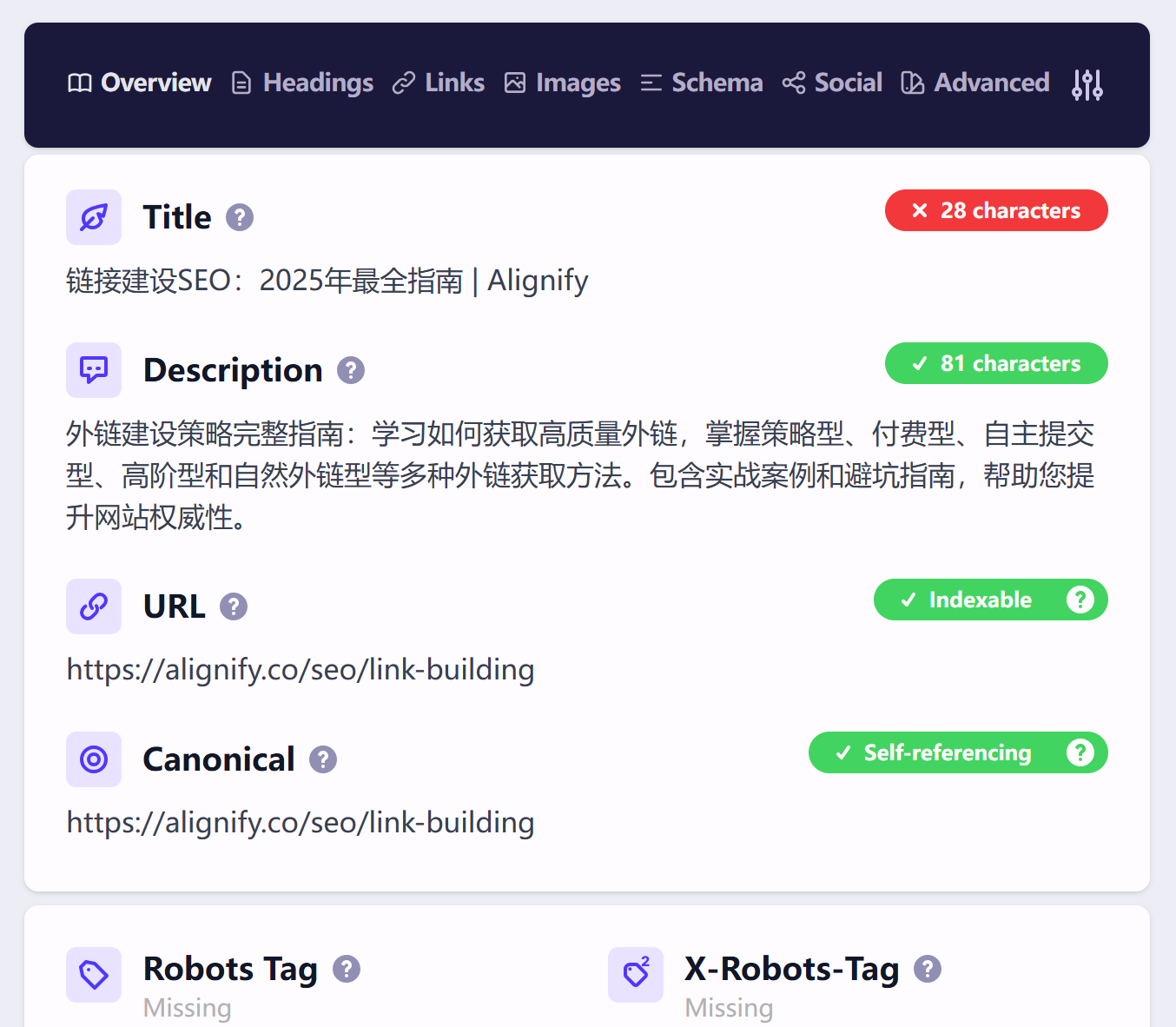
Third-Party SEO Tools: Professional SEO tools like AITDK and Detailed can view page Meta Tag information in detail. These tools not only display Meta Title and Meta Description but also provide other metadata information, helping comprehensively understand page SEO configuration.
Manual Checking
Beyond using tools, you can manually check Meta Tags. Search your website pages in Google, check if displayed titles and descriptions in search results match expectations. If displayed titles or descriptions aren't your set Meta Tags, Meta Tag configuration may have issues, or Google may have selected other page content as title or description. Regularly check important pages' search result display effects to ensure Meta Tags work correctly.
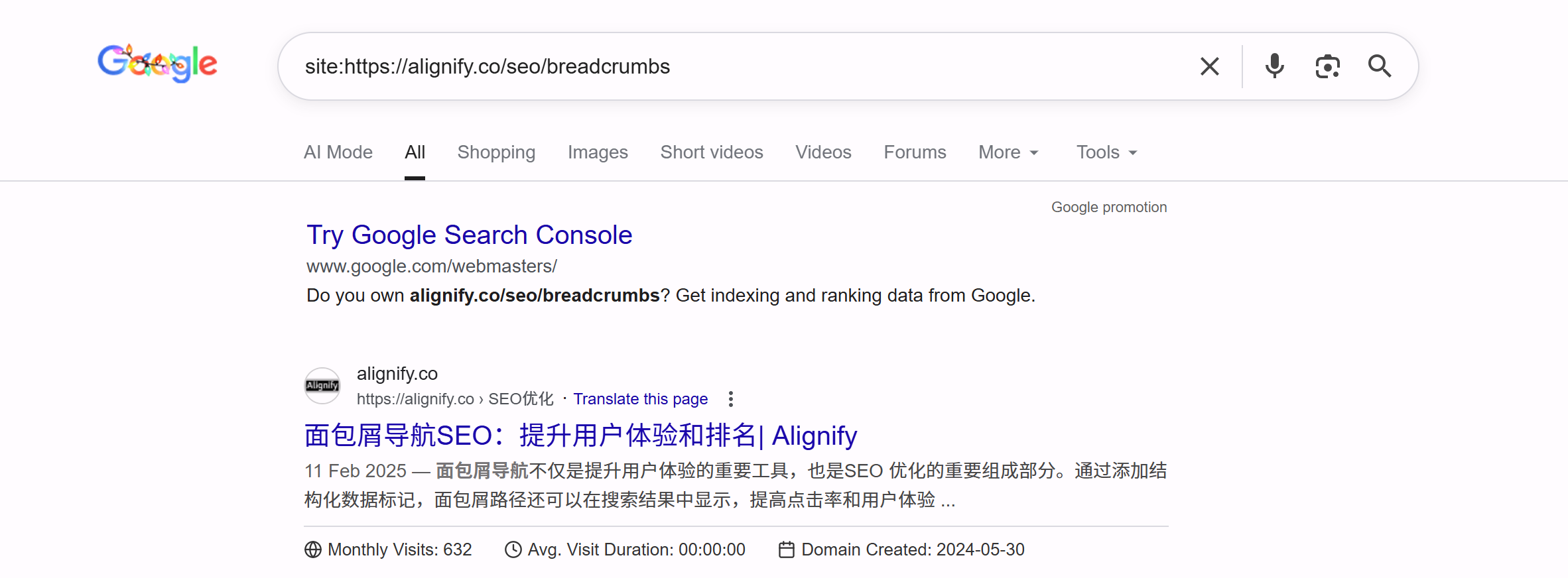
Site Command Query: In Google search, use the site:yourdomain.com command to view all pages of your website indexed by Google. Clicking search results shows Google's actually displayed Title Link and Description, helping verify if Meta Tags are correctly configured and if Google uses your provided Meta Tags.
Mobile Testing
Use browser developer tools' device simulation to check Meta Tag display effects on mobile devices. Ensure important information fully displays on mobile, avoiding truncation. Also search and view search results on real mobile devices to verify Meta Tag actual display effects.
References
- Semrush. "Meta Tags: What They Are & How to Use Them for SEO." https://www.semrush.com/blog/meta-tag/
- Google Search Central. "Special tags that Google understands." https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/special-tags
- Search Engine Land. "SEO meta descriptions: Everything to know." https://searchengineland.com/seo-meta-descriptions-everything-to-know-447910
- Ahrefs. "SEO Meta Tags: The Ultimate Guide." https://ahrefs.com/blog/seo-meta-tags/